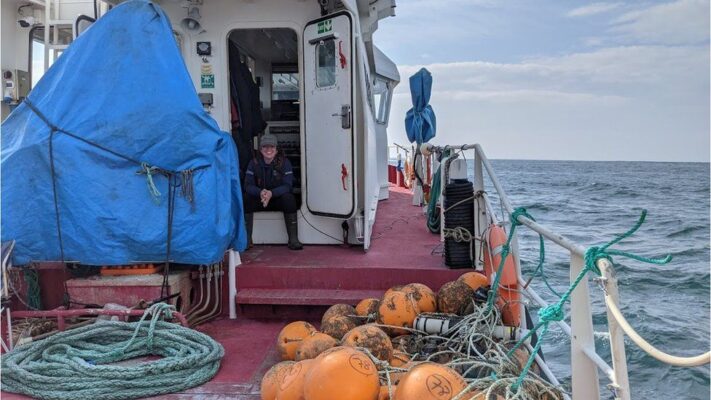

The OTN researchers have been working to maintain SeaMonitor’s underwater infrastructure
It is part of the SeaMonitor project that’s tracking a number of species, including Atlantic salmon, basking sharks, harbour seals, flapper skate and cetaceans.
SeaMonitor, led by the Loughs Agency which refers to it as “Europe’s largest fish counter”, uses acoustic telemetry technology to listen to life under the sea.
Over the last week, fieldworkers from Canada’s Ocean Tracking Network (OTN) have been servicing the project’s underwater technology.
“This is the first time that the Ocean Tracking Network team has travelled internationally since the beginning of the pandemic,” said OTN’s Cassandra Hartery.
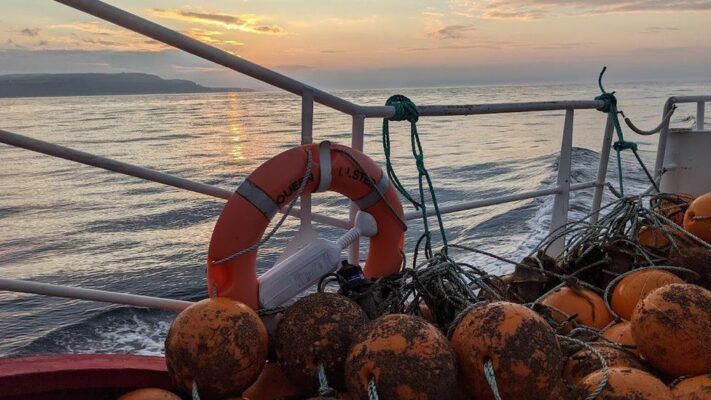

The SeaMonitor project is tracking the movement of five species in the Irish Sea
“It has truly been an unforgettable experience.”
SeaMonitor’s sub aqua listening stations stretch from Malin Head in Ireland to the island of Islay in Scotland.
They record transmissions from a variety of marine species tagged by scientists.
Launched in 2019, SeaMonitor involves eight international research partners, including OTN, based at Dalhousie University in Nova Scotia.
Cassandra and her OTN colleague Caitlin Bate have been based in Derry and Ballycastle in recent weeks.
Caitlin says the “globally important” project will help develop a better understanding of life in the Irish Sea.
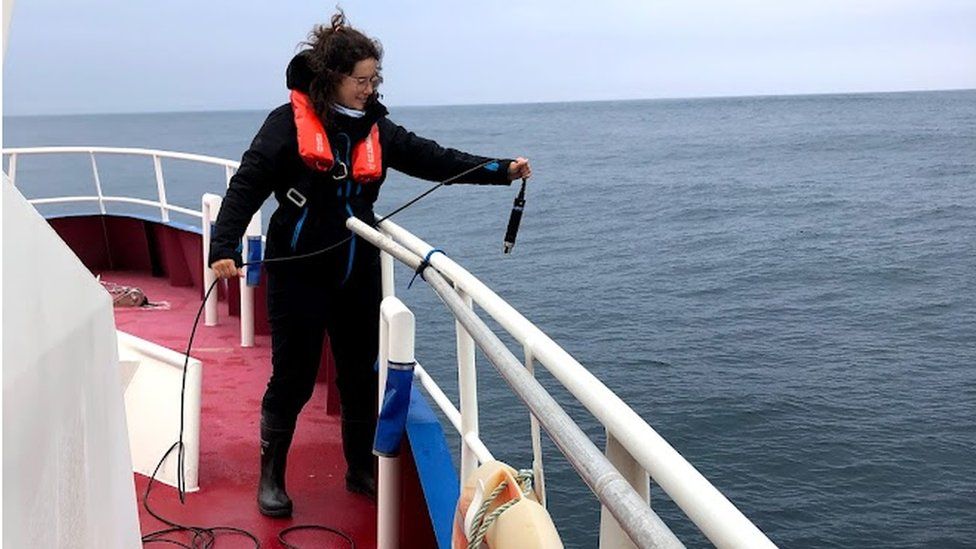

The acoustic technology allows researchers to listen to life under the sea
The project’s research “will be used to protect these populations in the near future and also for generations to come”.
Researchers from Northern Ireland, Scotland, the Republic of Ireland, the USA and Canada are all involved.
That collaboration is significant, Cassandra adds.
“It not only demonstrates the impact of multi-national marine tracking through the creation of a shared infrastructure, but it’s also allowing scientists from partner countries to conduct much larger-scale studies than they were able to do before.”
The project’s principal officer, Ross McGill of the Loughs Agency, says little is still known about many of the species’ sub aquatic movements.
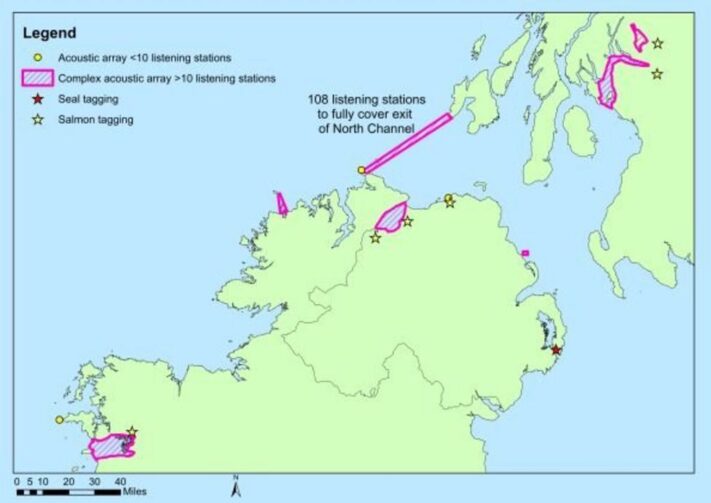
SeaMonitor’s listening stations stretch the Irish Sea
“The data collected will allow us to understand the pressures vulnerable species like Atlantic salmon and basking sharks face so that we can then translate that knowledge into management plans and policies to better protect them.”
SeaMontior’s findings – including specific management plans for the Foyle and Clyde rivers’ salmon populations – are due to be published in early 2023.
Tags:




